The team led by Dr Paulina Pruszkowska-Przybylska conducted a study among 182 residents of Lodz (106 women and 76 men) aged 38-64. The study consisted of three main parts: a survey, measurement of anthropometric measurements (finger length), and methylome analysis using blood samples from the study participants. Epigenetic age and its acceleration were calculated using several commonly used algorithms, known as epigenetic clocks (including PhenoAge and DNAmTL).
Mysterious 2D:4D Code
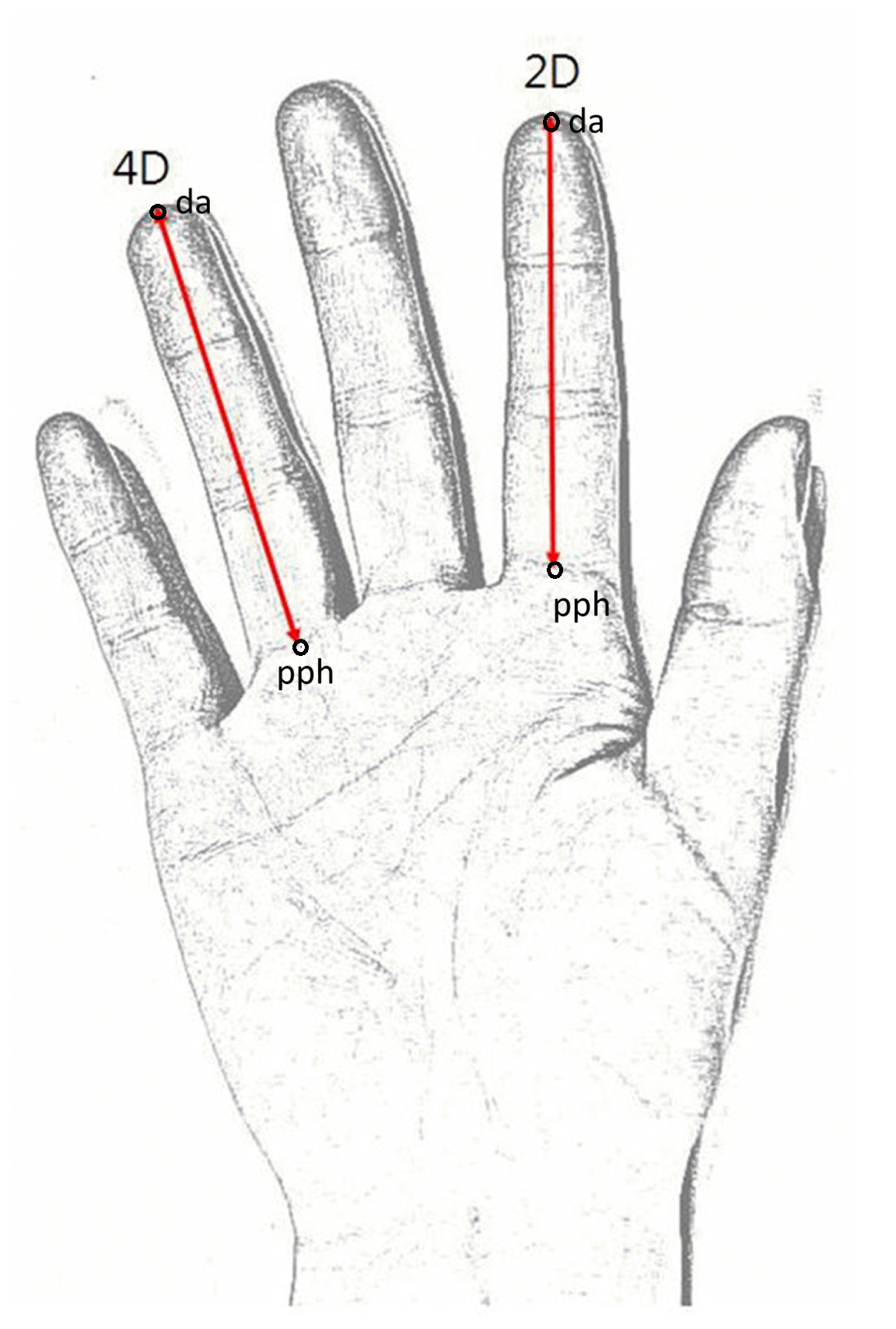
The previously mentioned female left-hand finger length pattern means, in practice, a higher ratio of the second (index) finger to the fourth (ring) finger (2D:4D). This pattern is dependent on the amount of sex hormones that affect the human body during foetal life
– explains Dr Paulina Pruszkowska-Przybylska.
The study found a statistically significant association between a higher 2D:4D ratio in the left hand and accelerated epigenetic ageing. It should be noted that this effect only affected men. This suggests that prenatal exposure to estrogen in men may influence the rate of ageing later in development.
Pregnant woman's lifestyle and its impact on 2D:4D
The 2D:4D ratio has been widely used in anthropology and human biology for many years. It is used, among other things, in research on the influence of the prenatal environment on adult development.
Numerous studies show that a mother's lifestyle during pregnancy, such as smoking or a poor diet, can lead to endocrine disruptions, which translates into hormonal levels in the environment in which the foetus develops. This, in turn, can influence changes in the 2D:4D ratio and subsequent development
– underlines Dr Paulina Pruszkowska-Przybylska.
Epigenetic age, or the biological age of our body
In addition to measuring finger length, researchers have also analysed epigenetic age, which is the actual ageing of cells, tissues and organs, which may differ from our chronological age. This age is determined by analysing epigenetic changes in DNA, called methylation. Methylation is a fundamental biochemical process in DNA that is responsible for many processes related to human development – particularly the formation and maintenance of appropriate tissue specification. Assessing epigenetic age can also help predict the risk of many diseases and track the effectiveness of lifestyle changes.
The study used a set of several epigenetic clocks, including PhenoAge and DNAmTL, and the conducted analyses showed that in men, a higher 2D:4D ratio was associated with a higher epigenetic age.
The conclusions drawn from this research can be used in prenatal prevention. There is a potential chance that identifying and eliminating harmful factors could reduce the risk of accelerated ageing
– Dr Paulina Pruszkowska-Przybylska assesses.
A detailed description and conclusions from the study can be found in the publication: Potential Predictor of Epigenetic Age Acceleration in Men: 2D:4D Finger Pattern. Additionally, Dr Paulina Pruszkowska-Przybylska discusses this discovery in the article: : Z długości palców można wyczytać, jak szybko się zestarzejemy [Finger Length Can Tell How Fast We Age], and in the podcast: Eureka. Czy w XXI wieku istnieje jeszcze miłość? [Eureka. Does Love Still Exist in the 21st Century?]; Jaka jest zależność między długością palców, a tempem starzenia się? [What is the Relationship Between Finger Length and the Rate of Ageing?] European Heritage Days.
